Owner: Kylie Battles | Publication date: 24 June 2022
Field of expertise:
Methods:
Application area:
Industry:
About the company
HuMoTech makes high-performance tethered robotic prosthesis and exoskeleton emulator systems. These systems enable users to have the physical sensation of wearing prosthetic devices without actually manufacturing and fitting each physical product. This process results in rapid evaluation of design concepts for R&D teams. Also, it ensures cost-effective, evidence-based prescriptions that enable patients to test different devices easily.
Challenges
In development area of robotic prosthesis, it is impossible to succeed without using mechanical FEA. In such area of design work, open-ended requirements are often come upon, such as minimizing or maximizing a part’s weight or stiffness. Improvement in healthcare, hopes and dreams of prosthetics users are constantly pushing the boundaries of what is possible. Certainly, simulation is the only way to significantly lower the high cost of trial-and-error process.
Technology used
Engineering solution
Engineers at HuMoTech successfully overcame their challenges by using Ansys Mechanical software for real-time assessment of prosthetics. Some of the features were especially useful. Firstly, assembly simulations with considering preloads allowed more realistic results. Also, mesh control and refinement enabled shortening the simulation time. Moreover, contact definitions helped obtain realistic stresses between different parts. This was very useful especially for parts where large elastic deformations appear. In addition, by conducting fatigue analysis, estimates of system components lifetime was improved. Consequently, users could be informed about when parts should be serviced.
Benefits
Prosthesis end-effector’s weight was reduced by 25%, which further allowed the device to emulate a wider range of prosthetic devices more accurately. Productivity at simulation set-up and calculations was increased, which enabled conducting more detailed analyses. Confidence that the parts would be robust in harsh conditions throughout years of use was gained.
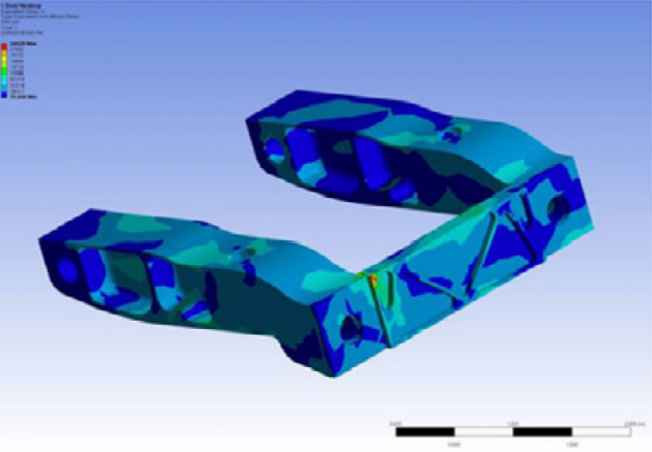
Assembly simulation of the prosthetic forefoot sides
and crossbeam under maximum user loading
against the dorsiflexion hard stop loading configuration
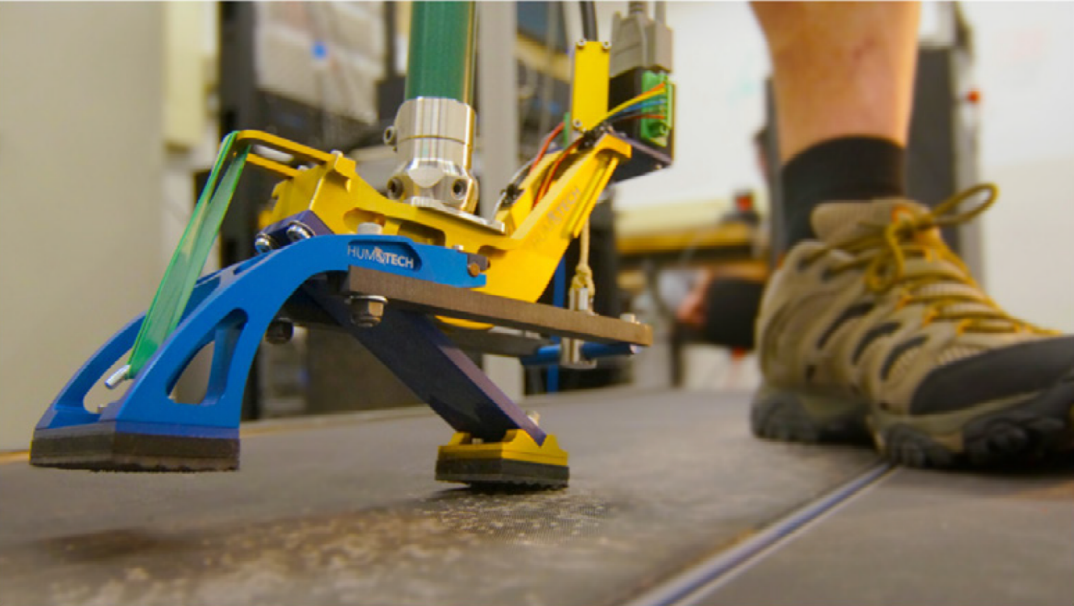

HuMoTech’s prosthetic foot worn by a user
with unilateral transtibial amputation