Owner: Matt Ladzinski | Publication date: 2022.09.15.
Field of expertise:
Methods:
Application area:
Industry:
Fire Engineering
Fire safety engineering is important from the viewpoint of fire prevention, life saving (smoke management, fire and smoke propagation, evacuation) and minimizing damages (fire extinction, firefighter protection).
If a building can be modelled with great accuracy and the origin, also transient fire and smoke behaviour can be described in a reliable way, we can predict different scenarios and redesign the building to resist extreme situations better.
We run a numerical simulation modelling the behaviour of the structure, objects, interactions, air, gases and fire with complex material properties laws providing accurate description of the evolution of solids, liquids and gases.
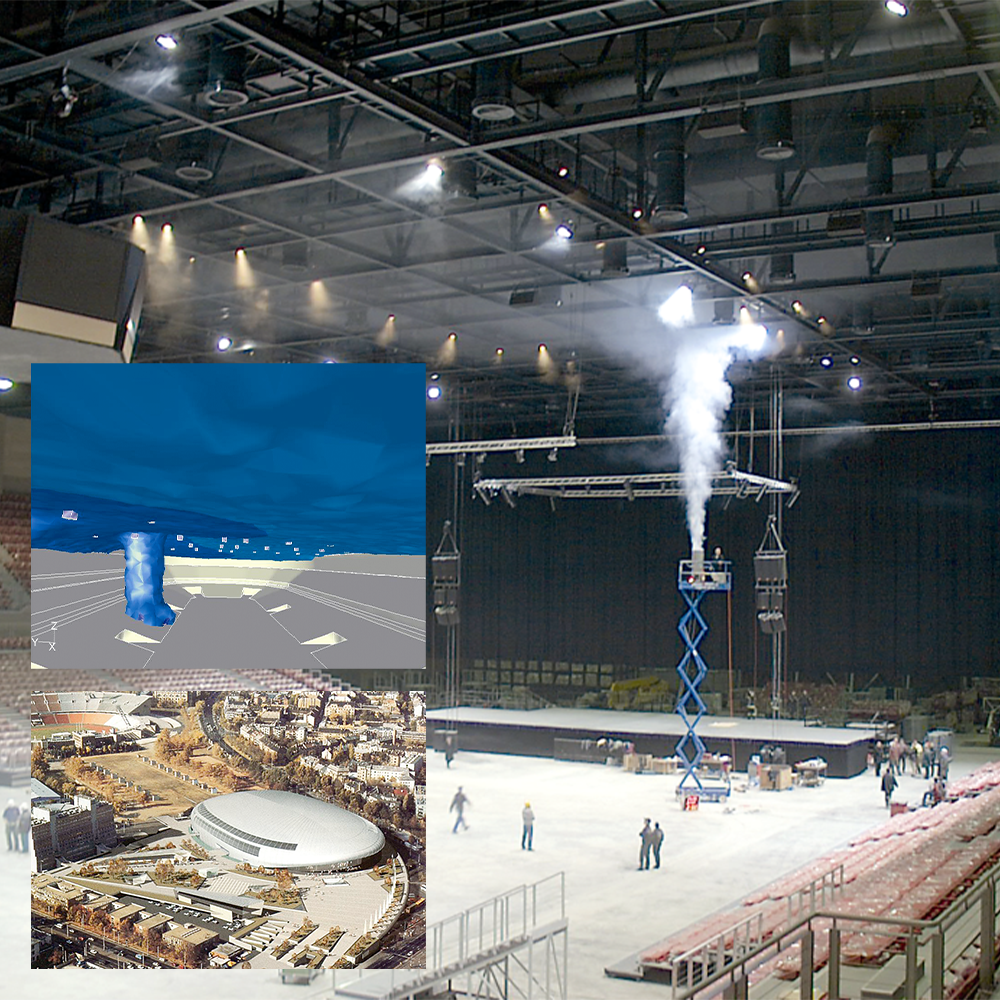
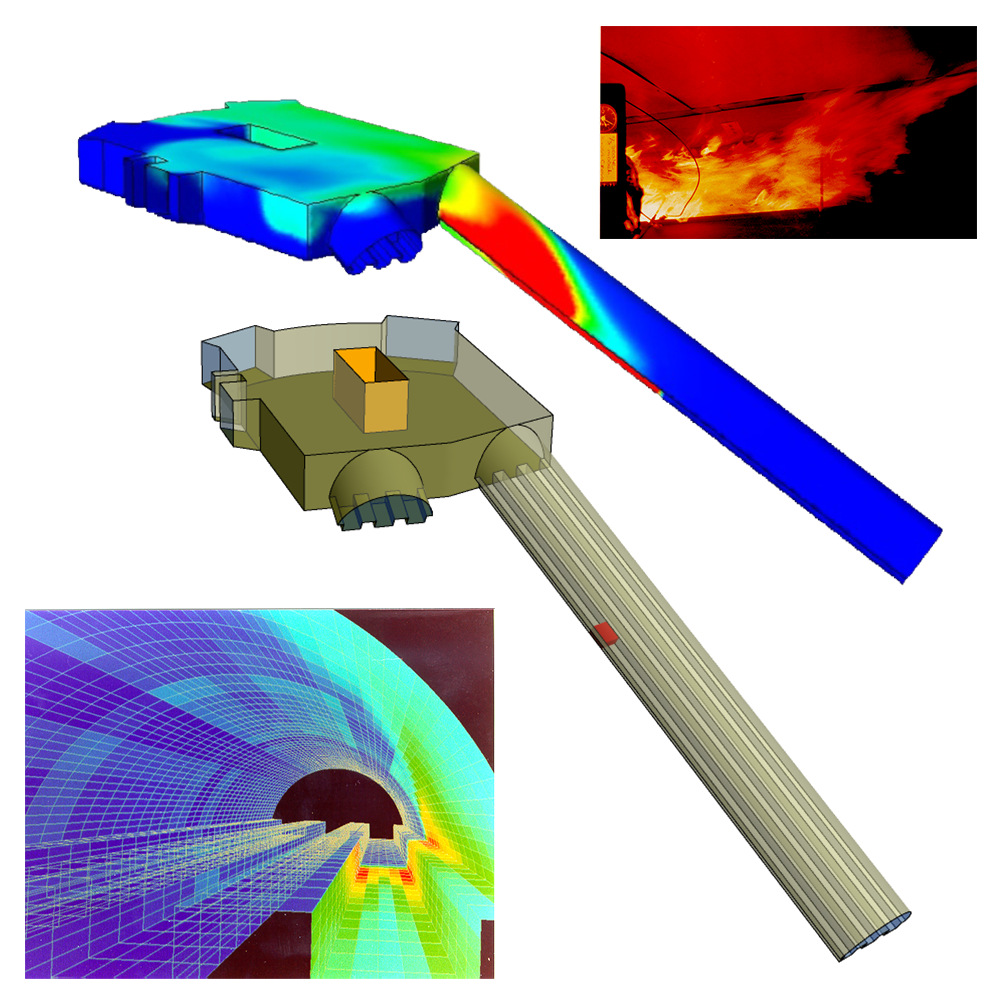
Complex Geometries
We should include the entire building and its surroundings to model better the consequences of the fire event on people and properties. Fire simulation is a complex method. It uses turbulence, chemical reactions, flame front tracking, heat flux monitoring and radiation. Moreover, it can be broadened with thermal-mechanical components.
Kings’ Cross fire accident, UK, 1987
A numerical simulation of a fire in an escalator tunnel of an underground metro station was carried out. A 1.6 MW fire emerged in a 45 m long line tunnel with inclination of almost 45°. Ansys CFD predicted the “Trench Effect” and temperature distribution. The official enquiry accepted this prediction.
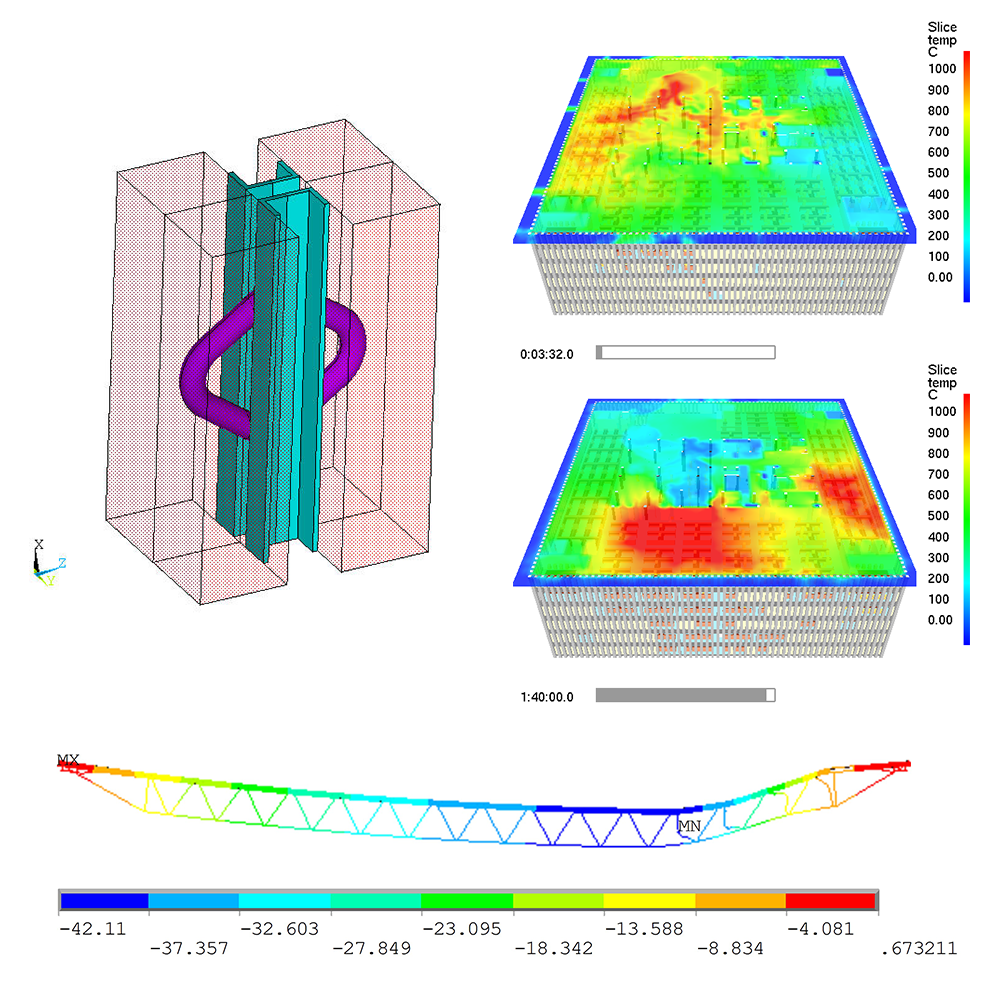
Tenability of structures
Additionally, it is possible to treat the fire origin which is caused by an explosion or a major impact and the structure suffers serious damage. We use a thermo-mechanical fluid structure interaction, where the impact weakens the structure and keeps it under an intense fire for a long period of time. We can include also the deterioration of the structure in the model. This way we can identify possible evacuation routes and time before collapse.
World Trade Centre, USA, 2001
Comprehensive investigations of the collapse of the World Trade Centre have revealed the fire induced thermal states and structural failure after a thorough analysis.
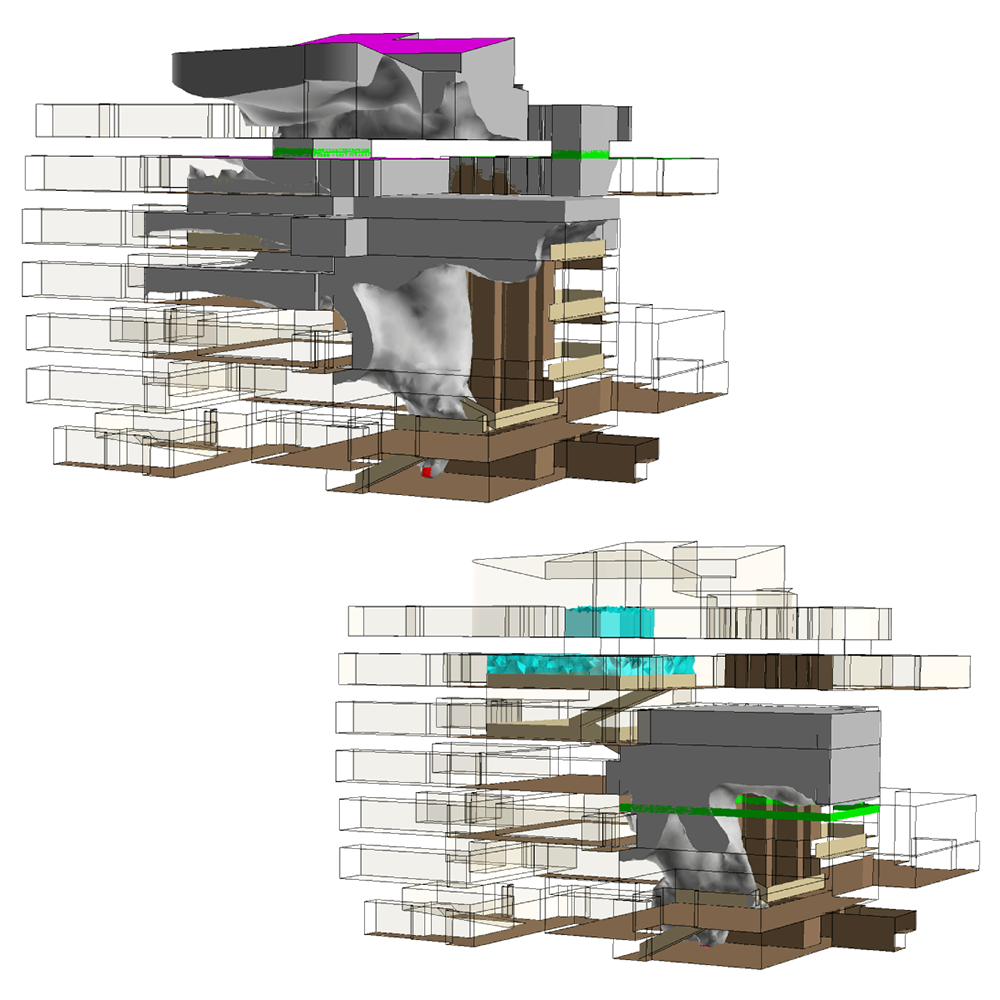
Smoke propagation
We can model the effects of the geometry on smoke propagation, as well as the evolution of visibility. Usually, large areas are broken down into smaller zones with the usage of curtains and emergency smoke management systems. Sectioning helps localizing the fire and prevent life damage.
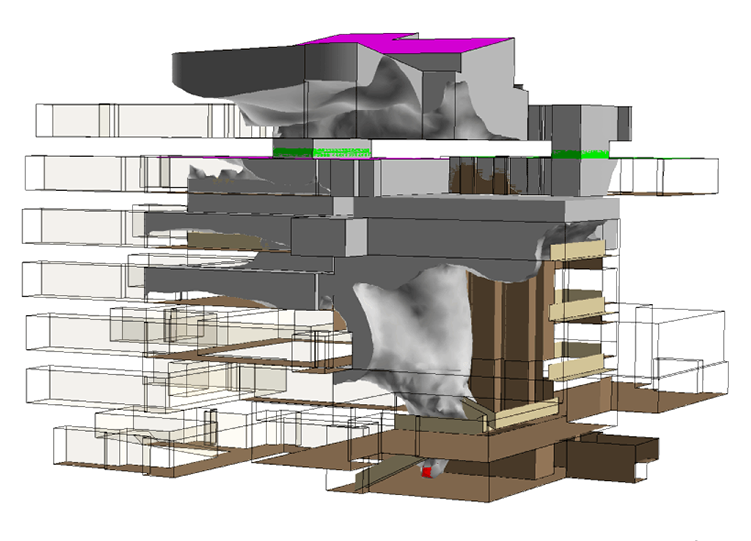
Smoke management in Complex Atria
Two scenarios were modelled in the complex structure. In the first model smoke could penetrate into many occupied areas of the building. In the second model a smoke management system that segregated the different parts of the complex, thus smoke penetrated a much smaller area.
Smoke extraction at airports
In the event of a fire at airports, an emergency smoke exhaust system will start to operate within one minute of detection. The system includes the deployment of emergency curtains, creating zones within the large indoor structure to control smoke spread.
“What-if” scenarios with virtual buildings
A virtual building allows us to investigate various disaster scenarios by the analysis of the evolution of the event with a necessary accuracy. We can also modify various structural, material and equipment properties.
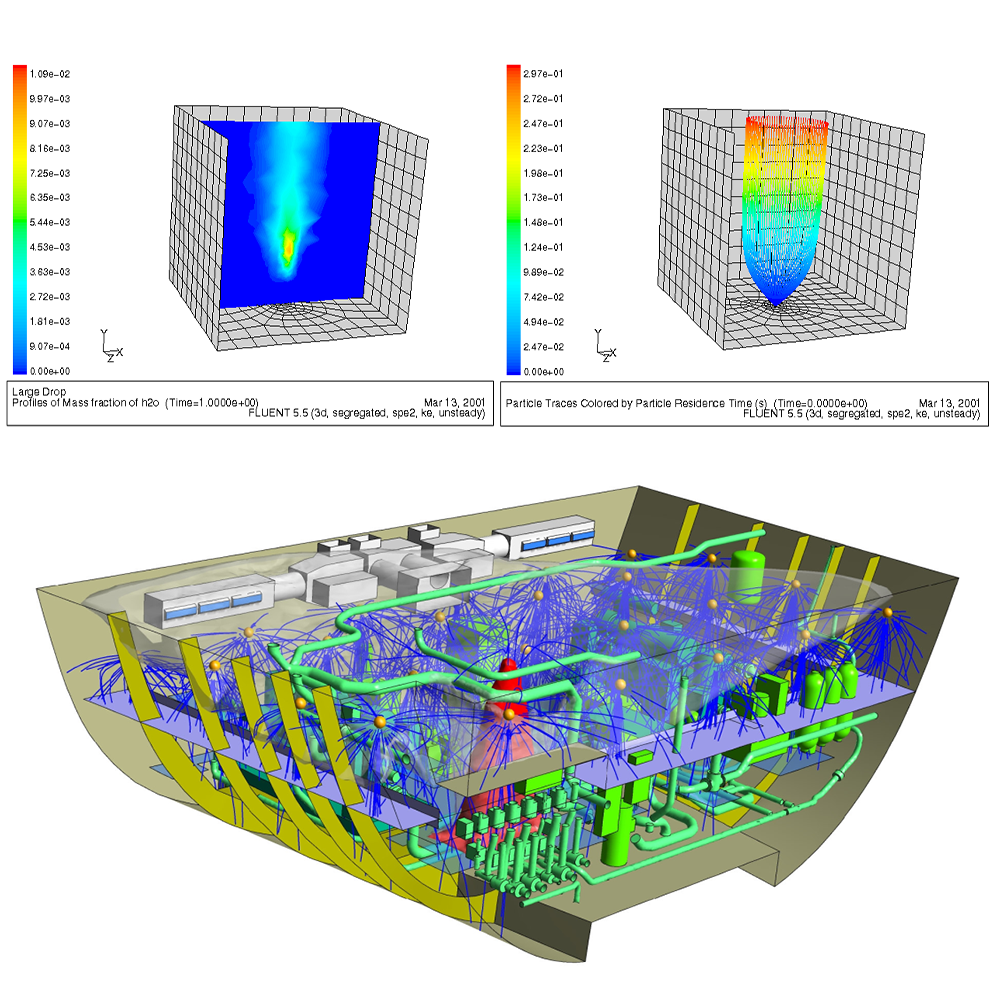
We can model droplet sizes of fire suppressing systems in complex geometries to optimize the effectiveness of fire suppression equipment. Also, in case of a fire event the dispersion of pollutants can be investigated in the close area of the building with the help of simulation.
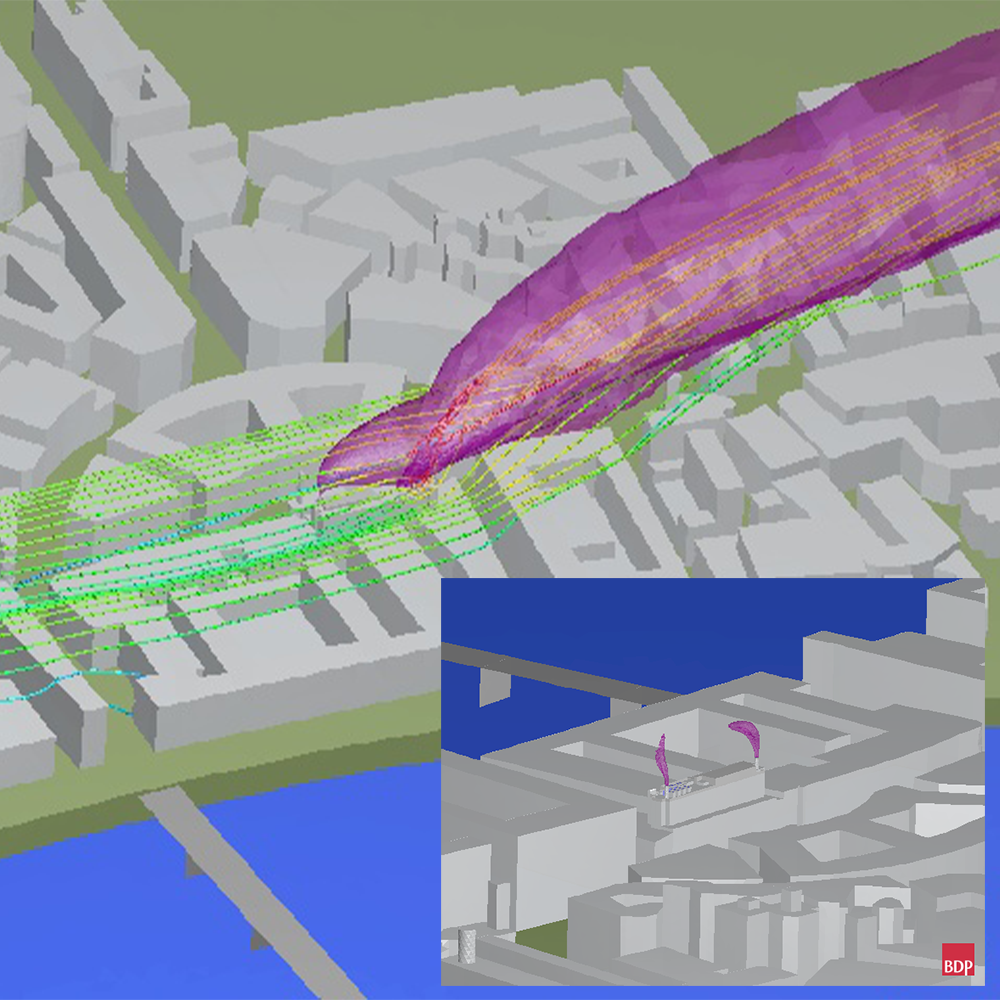
Pollutant dispersion near the River Thames, UK, case study
A fire event of a building was investigated. The simulation included other buildings within half a kilometre radius with the section of the River Thames. The model was run for a variety of prevailing winds. This way a detailed understanding of how the design would respond to different weather conditions was obtained.
Summary
Simulation is a cost-effective way to investigate numerous scenarios including extreme situations. It also provides additional information to fire engineers to take the necessary action to prevent disasters, save lives and properties.