The planned directive of the European Union will require a significant increase in the proportion of recycled plastic components in new cars, posing a major challenge for both the plastics and automotive industries. Can conscious design reduce the cost of using “green plastics“ in car parts?
The European Union’s planned Recycled Plastics Directive requires a significant increase in the proportion of recycled plastic components in new vehicles. This poses a major challenge for the plastics industry. Strict automotive quality requirements and current recycling capabilities leave relatively little room for maneuvering making cost-effective production difficult. The known challenges of this topic have been discussed at the recent Central European Plastics Meeting 2023, among others, and were also addressed in a previous article in Autopro Magazine (available in Hungarian). The solution is certainly complex, as the involvement of raw material producers, plastic manufacturers, recyclers, and legislators is all needed to achieve these goals. In addition, the role of car manufacturers (OEMs) and their suppliers is also not negligible. Avoiding unnecessary use of materials at the design stage and choosing materials that are easier to recycle can reduce additional manufacturing costs.
How does engineering simulation relate to this?
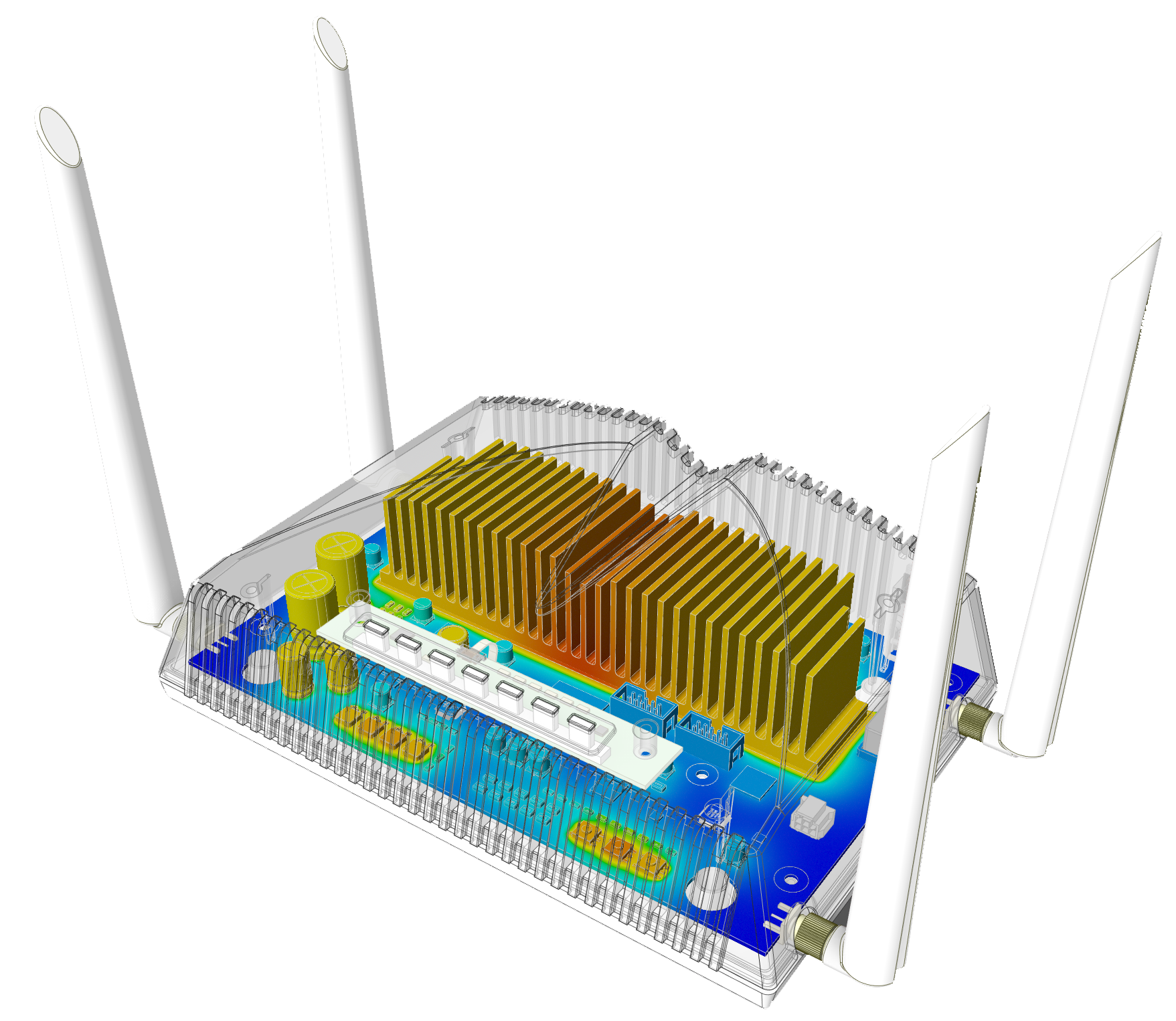
In the design phase, engineers can be assisted by the simulation tools and Econ Engineering provides services with professional expertise in this field. Different types of plastics have different material properties and using engineering simulations to investigate their effect on the behavior of a component can give a time- and cost-effective solution. Simulation can be used to identify material or design-related problems and help find solutions quickly, whether metal, polymer, or composite materials are used. Through appropriate material selection and virtual modeling, development, manufacturing, and reprocessing costs can be reduced, and development time and time to market can be shortened. However, this requires not only expertise but also a high level of cooperation between the different industrial players.
Injection molding simulation can be used in the early stage of the design phase to optimize processes, detect and prevent potential manufacturing errors, and minimize scrap before the actual manufacturing phase. Design changes can be easily made at this stage, supporting successful decision-making. Several physical forces act simultaneously on the vehicle components. Using complex, multi-physics simulation, the combined or separate effects can be examined virtually, without the cost and time of physical test campaigns.
Thus, the engineering simulation technology enables market players to predict whether their recycled plastic products will hold up under real-life conditions or if further options should be investigated.
Related data
In Europe, plastics production is approximately 360 tons/year, of which 10% is used in the automotive industry and nearly 40% in the packaging industry. 32.5% of the total production is recycled, most of which is easily recyclable plastic packaging waste. The forthcoming EU directive will require 10% of recycled plastic parts to be used in the car industry by 2025 and 25% by 2030, which is ambitious considering the recycling rate of all plastic waste. As a nuance to the picture, it is not yet clear whether this figure will apply per component or the total plastic weight of the car.